Understanding the impact of tariffs
The tariff announcements by the US administration at the beginning of April created a wide range of impacts across many industry sectors. However, the 90-day pause announced shortly after also suggests an intent by the US administration to negotiate, as well as providing a planning window for businesses to potentially review their dependency on key markets such as China.
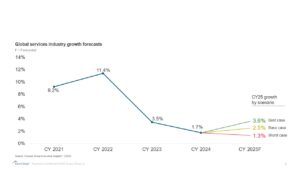
The impact of higher import tariffs in the US varies across industries, and is dependent on a number of factors including their overall reliance on tariffed raw materials, price elasticity, industry growth, margin health, and ready availability of alternative sources.
The current proposed tariff strategy encompasses two distinct objectives. The first – a 10% universal tariff – aims to stimulate domestic manufacturing. The second – which focuses on more extensive reciprocal tariffs – is intended by the US Administration to serve as a strategic tool to incentivize trade negotiations. Together, these measures seek to address imbalances in existing tariff structures according to the US Administration, although these purported imbalances have been challenged by existing US trade markets from around the world.
The stark reality is that industries that rely heavily on tariffed imports, have limited flexibility to adjust prices, and are already under financial strain leading to further pressure on both growth and profit margins. In contrast, sectors that have already adapted to alternative sourcing in response to past trade policies and have strong cost management strategies are likely to face minimal disruption.